The transformative power of 3D printing is undeniable. The use of 3D printing is rapidly growing in prototyping and design. Hence, it’s no surprise that 3D printing technology is also evolving to meet these demands that increase the usefulness and efficiency of this technology.
Polyjet Technology is a full-color 3D printing technology that combines the strengths of both plastic and powder-based technologies. Additionally, it delivers the best hybrid of power, speed, quality, reliability, and flexibility in one print. So, if you are looking for that extra edge for your prototype in terms of materials, aesthetics, and accuracy, Polyjet is the way to go.
Read on to learn everything about this innovative 3D printing technology for your current or future projects.
What is Polyjet?
Polyjet is a 3D printing technique and a patented invention of Stratasys. It is an additive manufacturing system. However, it works quite differently from other printing technology.
The Polyjet print head uses liquid photopolymers to create your models. It is similar to a regular inkjet printer. The difference, instead of ink on paper, Polyjet prints layer upon layer of the photopolymers on the build tray.
Polyjet printers can be as accurate as 0.1mm to create the smoothest surfaces and thinnest walls. Thus, making them ideal for producing prototypes with complex geometries. Furthermore, only Polyjet allows you to mix different materials. In short, you can combine rigid materials with flexible ones in the same print run.
Polyjet also supports an extensive range of colors and material combinations to produce incredibly realistic prototypes.

How Does Polyjet 3D Printing Work?
The Polyjet printing process typically has three main steps: pre-processing, production, and support removal.
In the first stage, you import your CAD file into the Polyjet 3D printing software. This is where you arrange the order of printing. Meanwhile, each photopolymer layer is jetted onto the printing plate and cured using a flash of UV light.
If you need multiple materials in one model or multiple parts printed in a single run, this is where you determine the size, colors, and support structures.
The production stage is where you hit the “print” button using the Polyjet printer and observe your prototype come to life. Polyjet printing is significantly faster than other 3D printing processes. The reason is, it deposits liquid resins onto the print bed rather than extruding the model from semisolid materials.
Finally, support removal. Where Polyjet gel-like support structures separate from the model, either by hand or using water. Usually, no other processes are necessary to cure a Polyjet prototype. Once it’s off the 3D printer and clean of support materials, it is ready for testing or use depending on the development stage.
Polyjet Technical Specifications
When designing your prototype for Polyjet 3D printing, always factor in the capabilities of your printer itself. Even if your CAD model is as accurate as possible, the final product is always subject to changes in shape, textures, colors, and finishes.
The Polyjet printing process alters the physical model but to a slightly less degree than other 3D printers. The following table of specifications is a good starting point when working with a Polyjet printer. Although it has these specifications, these are definitely not limitations of Polyjet 3D printing.
Instead, they are the framework that allow you to create any prototype.
| Accuracy | 0.1-0.3 mm (300 microns) |
| Layer resolution | 16 microns |
| X/Y resolution | 0.0017 in |
| Wall thickness (minimum) | 1 mm |
| Feature size (minimum) | 0.0012 in (0.3mm) |
| Part dimensions (normal resolution) | 19.3 x 15.35 x 7.9 in |
| Part dimensions (maximum) | 39.3 x 31.4 x 19.6 in |
| Shore hardness range | 27 A to 95 A |
| Finishes | Matte, glossy, and custom finishes depend on the type of materials. |
Materials Used in Polyjet 3D Printing
Thousands of material combinations are now available with Polyjet printing that are impossible to achieve in other types of 3D printing. Now, you can combine materials, features, textures, and colors to create stunningly realistic prototypes or models.
Polyjet offers eight distinct types of materials with unique qualities when used in single material printing or multi-jet, or hybrid printing.
1. Digital Materials
Digital material is a type of combined material in Polyjet 3D printing. Using multi-jetting 3D printers, you can print digital materials which can mix up to six different resins. Additionally, the prototypes can be as detailed and complex as necessary. Therefore, allowing you to unleash your creativity and achieve desired outcomes. These flexible or rigid materials can support hundreds of thousands of color options too.
2. Digital ABS Plastic
Digital ABS plastics are stronger and more heat resistant than regular ABS plastic. Prototypes made from this material can have very thin walls but with better dimensional stability. Electrical parts, engine parts, smartphone cases, or any product that needs to snap to fit can be 3D printed using digital ABS plastic, making it suitable for products that require snap-fit connections.
3. Rubber-Like Materials
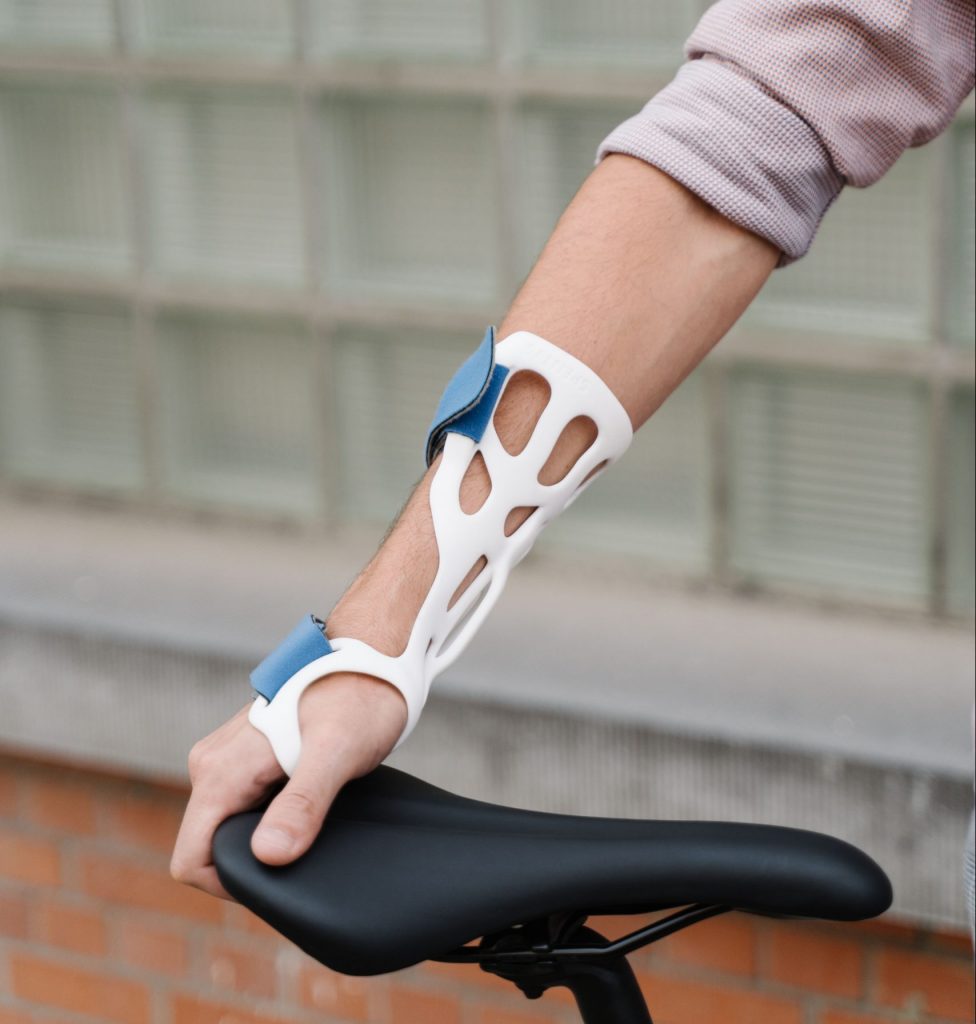

Prototypes that need a level of flexibility or soft coatings can be 3D printed using Polyjet rubber-like materials. These prototypes include products that need nonslip surfaces, soft-touch grips and handles, gaskets, seals and hoses, and even footwear prototypes. Also, you can combine rubber-like materials with rigid materials to produce a range of Shore hardness values ranging from A 27 to A 95.
4. High-Temperature Materials
With high-temperature Polyjet materials, you get excellent dimensional stability in prototypes and models exposed to heat. You can combine high-temperature materials with rubber-like materials to enhance their insulation properties and improve hardness and flexibility. High-temperature Polyjet materials are excellent for functional prototypes that have to withstand a lot of heat or function in demanding lighting conditions.
5. Transparent Materials
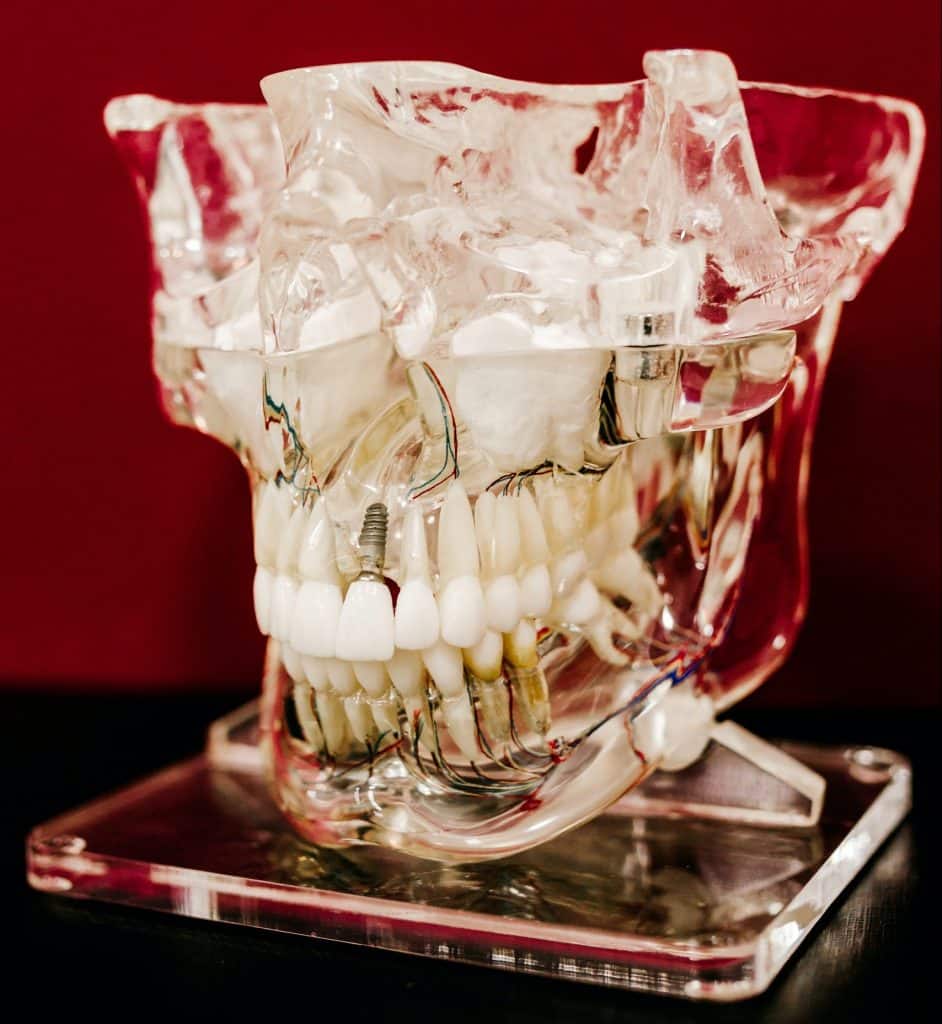
Polyjet transparent materials are great for prototypes that need see-through parts. You can also add colors to the transparent materials to get a wide variety of tint options for your model. These materials are ideal for prototyping glass products, eyewear, product cases or covers, as well as various medical applications such as contact lenses and clear dental aligners.
6. Rigid Opaque Materials
If you’re looking for the broadest possible range of color options for your prototype, Polyjet rigid opaque materials are worth exploring. When combined with rubber-like materials, they enable the creation of moving or assembled parts and electronic components . Additionally, they result in products that must feel soft to the touch and have a vibrant appearance for easy identification
.
7. Simulated Polypropylene Materials
Simulated Polypropylene materials replicate the qualities and appearance of polypropylene. For example, this type exists in things like product packaging, laboratory equipment, car components, living hinges, sound speakers, and plenty of other applications. If you’re looking to test or exhibit a polypropylene prototype, create a 3D simulated polypropylene prototype before proceeding to full production.
8. Biocompatible Materials
Polyjet biocompatible materials meet the required approval for medical use based on five key factors. These factors include genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, delayed hypersensitivity, irritation, and USP plastic Class VI compatibility. Using these materials, you can create colorless prototypes that need short-term exposure to mucosa membranes for up to 24 hours. In addition, you can also create prototypes that will be in contact with the skin for durations exceeding 30 days.

Polyjet 3D printers
A wide range of Polyjet 3D printers is available today, from small, compact sizes to large-scale industrial printers. Here are few examples:

Objet30 V5 series
The Objet30 V5 series is the smallest, and they come in the Pro and Prime versions. These printers print single materials plus support materials, similar to the slightly larger J55 model.

Objet Connex1 series
Other single-material printers include the Objet Connex1 series that come in the 260 and 500 models. You can print digital materials using the Objet Connex3 series printers (260, 350, and 500 models).

J8 series
This series offers an unlimited number of composite materials and over 500,000 color options. J4100 is the largest Polyjet printer, which allows a maximum model weight of 135kg on the printing plate.
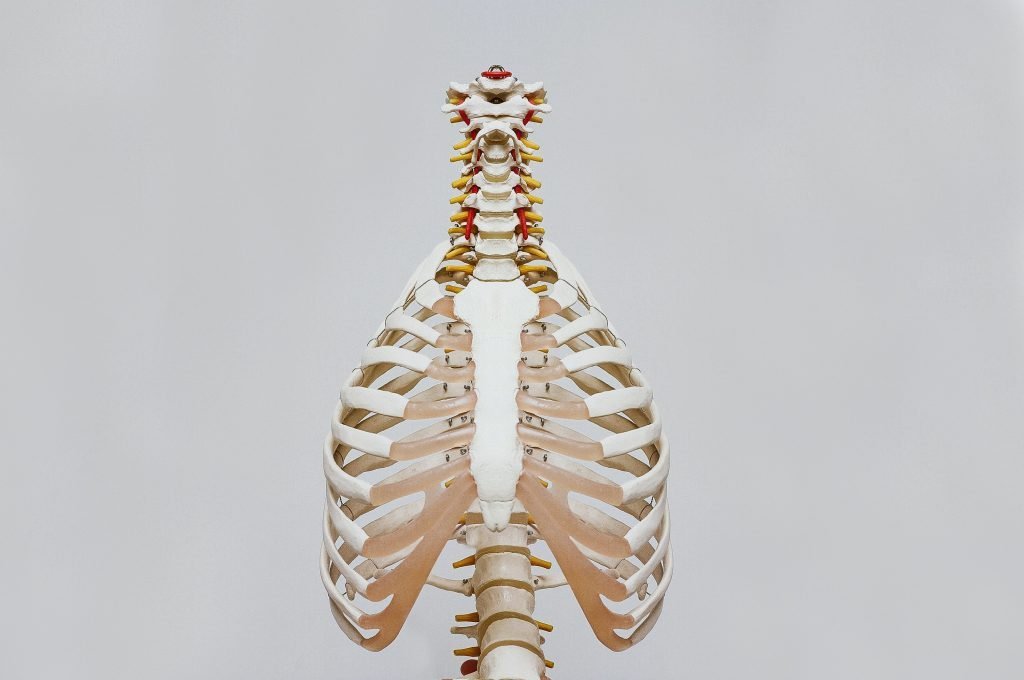
The most highly specialized printer in this series has to be the J750 Digital Anatomy printer which can produce highly realistic bone and tissue models. It also uses a gel-like support material that is easy to remove from blood vessel models without altering the delicate prints.
How to Choose
The biggest factor in choosing a Polyjet printer is the materials you want in your prototypes. A compact Polyjet 3D printer is more affordable when using single materials. Moreover, it delivers the best resolution and surface finishes for its size.
If your model requires multiple materials, larger stand-alone Polyjet printers are ideal. This is because they feature multi-jetting technology. There are three main ways to use this hybrid 3D printing feature;
- You can mix several materials into one model or one part of a model,
- Blend separate materials to create a brand new one, or
- Use mixed trays such that one print run can produce multiple individual parts printed using different materials.
Ultimately, it is your end goal that determines your choice of a Polyjet printer. Are you looking for a delicate, flexible prototype for a surgical implant? Or a series of complex moving parts for a robot? Or an entire fashion brand featuring 3D designs? Polyjet 3D printing can precisely produce what you need faster than other 3D printing options.
Advantages of Polyjet 3D printing
Polyjet 3D printing has four significant advantages for product designers, engineers, medical professionals, and artists in their creative and manufacturing processes.
1. Save At Least 50% Of Your Time
We have highlighted that Polyjet printing is fast, and the prototype is ready to use as soon as it comes off the printer. Hybrid printing also means that you can print several objects on one print run or combine several materials into one prototype.
This translates into more time for designing, testing, and perfecting the prototype. Therefore, leading to a faster route to full-scale manufacturing and marketing.
2. Realistic Models for Medical Applications
Anatomical models used for teaching and planning surgeries must be as close to real-life as possible. The material combinations offered by the Polyjet system can make 3D printed models. These models will not only look realistic but also feel and respond as the human body does. As a result, it improves the health outcomes for patients because their doctors receive better training. On top of that, their implants and prosthetics are thoroughly tested and simulated beforehand.
3. High Accuracy
The more accurate and detailed a product’s design is 3D printed, the more precise its final prototype will be. Whether you want a perfectly smooth, polished product or complex, intricate details down to the microscopic level, the Polyjet process precisely produces the desired outcome.
4. Multi-Material Capability
Digital materials, resulting from the blending of multiple resin types, offer designers and engineers unprecedented creative opportunities. As a result, you can build robust prototypes without compromising flexibility, textures, or colors. No other 3D printing technology can do this aside from Polyjet.
Now that we have seen what the Polyjet process is all about, it is worth comparing it against two other types of 3D printing, SLA and FDM.
Differences Between Polyjet and SLA
Stereolithography (SLA) is the oldest technology in the 3D printing industry. The only similarity between SLA and Polyjet is that both use a liquid resin that turns solid when exposed to UV light. The main difference is in the printing process. Meanwhile, SLA printers extrude the object out of a pool of resin, producing the object upside down. In contrast, Polyjet printers deposit the resin onto the build plate, eliminating exposure to hazardous resins and building the object from the bottom up.
Moreover, SLA printers work with a single material per print run. On the other hand, Polyjet allows the use of multiple materials and printing multiple objects in a single run.
SLA models also print breakaway support materials, which require sandblasting or washing in an alcohol bath during post-curing. However, the gel-like support materials produced in the Polyjet process can be easily removed by hand or with water, saving time on post-curing.
Differences Between Polyjet and FDM
Both fused deposition modeling (FDM) and Polyjet printers build models layer by layer. However, FDM printers deposit heated thermoplastic filaments on the printer bed that cool and solidify to create these layers. In contrast, Polyjet printers use liquid photopolymers cured using UV light.
FDM also uses a limited number of materials, mainly ABS, ASA, PC-ABS, and polycarbonate. On the contrary, Polyjet uses a variety of digital materials for a wider range of applications.
FDM materials are in a semisolid state during 3D printing. However, the finished models are generally sturdier and more durable but are limited in their flexibility and detail. Differently, Polyjet printing delivers more details because the resins are in a liquid state.
Factors to Consider When Using Polyjet 3D Technology
Polyjet technology is applicable to various products. This includes prosthetics, implants, mobility aids for healthcare, architectural models, robotics prototypes, interlocking structures and tools in industrial manufacturing, and customized designs for automotive, cycling, and aerospace parts.
With all these options on the table, it’s essential to understand which materials and processes are best for each specific product type. So far, we have discussed the features and advantages of Polyjet printing, so let’s consider the four main questions to determine if Polyjet printing is suitable for you.
How Will Your 3D Model Be Used?
Before printing your 3D model, keep in mind the end use or purpose of the product. Polyjet technology is renowned for its flexibility and ability to produce intricate details. Therefore, it lends itself to medical applications and geometric designs for mechanical parts.
Nevertheless, if aesthetics is a key factor, for example, in creating product packages, footwear, eyewear, or artistic exhibitions, Polyjet is the best option. If you need a combination of robustness and aesthetics, the Polyjet process allows you to achieve this balance.
Which Material Is Best?
Before Polyjet technology, early 3D printers relied on a single material, usually plastics. The reason is, it produced rigid, sturdy products with a limited range of color options.
Now, Polyjet frees you to explore textures, colors, and flexibility. As a result, it will enable your end product to meet and exceed end-user expectations. Do consider the cost of producing digital materials because single materials are generally more affordable than hybrid materials.
Which Is the Best Type of Surface Finish?
Tools and components for mechanical or industrial applications demand a different type of finish compared to medical parts or packaging products. For pieces that snap to fit, a smooth finish is excellent. At the same time, a nonslip finish is best for handheld products, mobility aids, and footwear.
What Is the Size of The Prototype?
Polyjet has a maximum part size of 19.3 x 15.35 x 7.9 inches in a single printing run. Consequently, for any parts larger than this, you can design separately and then fit together seamlessly after the printing process. Factor in the support materials in the CAD design to understand how to work within the dimensions of Polyjet printers.
Conclusion
Polyjet 3D printing combines liquid digital materials and dissolvable support materials with faster printing speeds to produce quality prototypes. This technology gives the finest resolution of all 3D printing technologies. Therefore, you can integrate smaller, more detailed patterns into each design. Additionally, one Polyjet prototype can feature different Shore hardness ranges, multiple materials, and a wide range of brilliant colors.
Ready to bring your CAD design to life? Get in touch with Jiga for a quick, comprehensive quote. We also give you access to Polyjet 3D printing professionals that will get your prototype ready in no time. Contact Jiga now.